Land contamination is one of the extensively addressed issues, which is gaining significance in lots of developed and growing nations. International efforts are actively envisaged to remediate contaminated websites as a response to adversarial well being results. Popular typical methodologies solely switch the part of the contaminant involving price intensive liabilities in addition to dealing with danger of the hazardous waste.
Physico-chemical strategies are efficient for particular wastes, however are technically complicated and lack public acceptance for land remediation. “Bioremediation”, is one of the rising low-cost applied sciences that supply the chance to destroy varied contaminants utilizing pure organic actions. Resultant non -toxic finish merchandise as a result of microbial exercise and insitu applicability of this expertise is gaining enormous public acceptance.
In the current research, composting is demonstrated as a bioremediation methodology for the stabilization of contaminated lake sediments of Hyderabad, A.P, India. Lake sediment contaminated with organics is collected from two stratums – higher (0.25 m) and decrease (0.5m) to arrange as Pile I (Upper) and Pile II (Lower) within the laboratory. Lime as a pretreatment to the lake sediments is carried out to make sure steel precipitation. The pretreated sediment is then blended with natural and inorganic fertilizers like cow dung, poultry manure, urea and tremendous phosphate as preliminary seeding amendments.
Bulking brokers like sawdust and different micronutrients are offered. Continuous monitoring of course of management parameters like pH, moisture content material, electrical conductivity, complete unstable solids and varied varieties of nitrogen have been carried out throughout your entire course of the research.
The stability of the compost was evaluated by assessing maturity indices like C/N, Cw (water soluble carbon), CNw (Cw/Nw), nitrification index (NH4/NO−3), Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC), germination index, humification ratio, compost mineralization index (ash content material/oxidizable carbon), sorption capability index (CEC/oxidizable carbon). Enzyme actions of agricultural curiosity like urease, phosphatase, β-glucosidase, dehydrogenase and BAA-hydrolyzing protease, that are concerned within the nitrogen, phosphorus and carbon cycles, have been additionally assessed.
Total content material of macro and micronutrients within the remaining compost was additionally decided to evaluate the fertilizer worth. The research revealed that composting might be utilized as a remediation expertise after eradicating the highest sediment. The maturity indices which might be evaluated from the current research can be utilized to validate the success of the remediation expertise.
Introduction
Sediments are typically acknowledged to play a distinguished function in ecosystem biking, as the highest layer is intimately linked to floor waters via bodily, chemical and organic processes. The steady discharge of industrial wastes into the water our bodies is rising the danger of their contamination [1]. Sediments are globally thought of the last word sinks for the particulate accumulation of organics and their environmental transformation in sediments has been nicely documented [2, 3]. Organic contaminants in sediment techniques are mixtures of a whole lot of aliphatic, chlorinated fragrant and different natural compounds, the relative proportions of which range significantly between sources [4]. Inorganic contaminants even have very complicated interactions with each anthropogenic and pure elements in marine sediments.
The persistence of organo xenobiotics within the setting is a matter of vital public, scientific and regulatory concern as a result of of the potential toxicity, mutagenicity, carcinogenicity and potential to bioconcentrate up the trophic ladder. These considerations proceed to drive the necessity for the event and software of remediation strategies [5]. It is now well known that contaminated land is a possible risk to human well being, and its continuous discovery over current years has led worldwide efforts to remediate many of these websites, both as a response to the danger of adversarial well being or environmental results brought on by contamination or to allow the positioning to be redeveloped to be used [6].
A key consider each the degradability and bioavailabiity of probably the most recalcitrant fractions of anthropogenic contaminants is the long-term sorption that may happen between natural molecules and clays or different minerals in soils and sediments [7].
Bioremediation of Contaminated Lake Sediments and Evaluation of Maturity Indicies as Indicators of Compost Stability
Bioremediation of Contaminated Lake Sediments and Evaluation of Maturity Indicies as Indicators of Compost Stability
Hyderabad, the capital metropolis of Andhra Pradesh, South India has nearly 80 lakes in and across the metropolis. With the rising industrial actions over time about Eight giant industrial estates have been developed and these industries are unscrupulously dumping their effluents into the close by lakes thereby depleting the pure flora, fauna and the ecological stability. The pollution in these lakes are likely to bioconcentrate up the trophic ladder and attain people. So, rejuvenation of these lakes is a activity of utmost significance and using physico-chemical processes solely remodel the pollution from one kind to a different however organic processes remodel them into innocuous finish merchandise. These considerations proceed to drive the necessity for the event and software of viable and low price remediation strategies [8]. Bioremediation is one such expertise that provides the chance to destroy or render innocent varied contaminants utilizing pure organic exercise. Micro organisms have a singular potential to work together each chemically and bodily with an enormous vary of each man-made and naturally occurring compounds resulting in a structural change to, or the entire degradation of the goal molecule [9].
Composting is one of the bioremediation methods which when carried out underneath managed situations within the presence of oxygen ends in the organic decomposition and stabilization of the biodegradable elements. The course of of composting contains 4 predominant phases, that are the preliminary part, the thermophilic part, the mesophilic part and the maturation part after which the compost can be utilized as an natural modification. For the compost for use as an natural modification it needs to be assessed for sure parameters like nitrification index, cation trade capability, germination index, humification index, water soluble carbon, compost mineralization index, and sorption capability index and many others.
Stabilization or maturation additionally implies the formation of some humic – like substances the diploma of natural matter humification is usually accepted as a criterion of maturity [10]. The humification course of produces practical teams and so elevated oxidation of the natural matter results in rise in cation trade capability. So compost with excessive cation trade capability is regarded as an index of maturity [11]. The diploma of maturity may also be revealed by organic strategies involving seed germination and root size [12]. Since immature composts could comprise phytotoxic substances such as phenolic acids and unstable fatty acids [13].
The purpose of the current work is to observe the method of composting for the contaminated lake sediments and observe the modifications occurring within the two piles arrange by taking sediment from completely different strata and discusses few of the maturity indices and thus validates their use as matured composts ensuing from the organic stabilization.
Materials and Methods
Initially a 100 × 100 m plot on the lakebed was chosen and the highest layer was dredged and despatched to a remedy storage and disposal facility situated close to the outskirts of metropolis for land filling thereby getting rid of the uppermost-polluted layer on the lakebed. The subsequent 0.25 m of the lakebed was eliminated and a portion of the sediment was arrange as Pile 1. An additional 0.25 m was dredged whose half was arrange as Pile 2. The two piles have been arrange by taking the sediments from two completely different strata of the lakebed in a view to evaluate the leaching potential of pollution into the completely different strata of the lake sediments and their amenability to composting. The soil kind on the lakebed has the next traits Clay – 352 gm/Kg; Silt (20–50μm) – 81 gm/Kg; Sand (50–200μm) – 61gm/Kg; Sand (200 – 2000μm) – 32 gm/Kg.
Pile 1 – Sediment from higher stratum:
Pile 2 – Sediment from decrease stratum.
Lime Stabilization
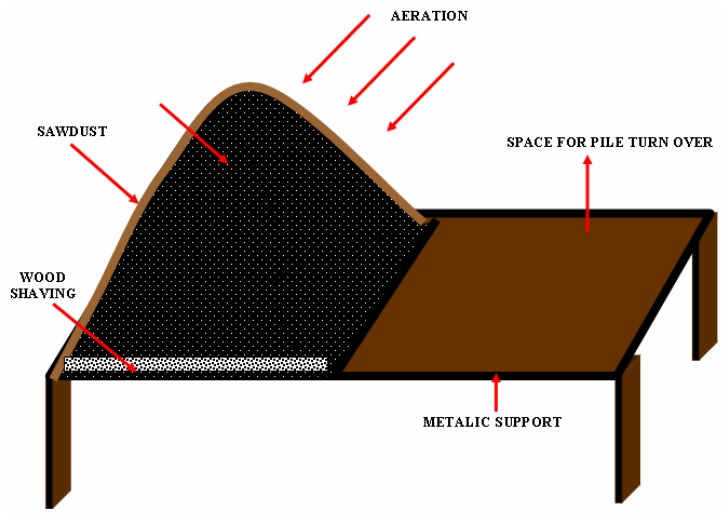
The polluted sediments from the 2 completely different strata have been initially blended with lime at 1% (w/w, dry weight foundation), which raised the pH to 9.2. Liming helped within the stabilization of heavy metals by precipitation as steel hydroxides at larger pH [14]. The organics and heavy steel focus within the sediments earlier than and after composting are offered in Table 1. The sediments have been saved as such for 5 days and then blended with natural amendments like manure (Poultry manure and cow dung) and sawdust, which introduced down the pH to six.8. Lab scale experiments for composting have been arrange by taking sediment, manure and sawdust within the ratio of 2:1:2 making a complete of 120kgs on dry weight foundation. The lab scale arrange for the cardio composting pile is proven in Fig. 1. The natural manure is excessive in nitrogen and is used for the adjustment of carbon/nitrogen ratio. Urea and superphosphate have been additionally added to take care of the preliminary C/N ratio in organising of the pile. Saw mud is used as a bulking agent to extend the porosity of the combination. The sediment was blended with the natural modification to take care of the whole solids content material between 35 – 45% and then homogenized. The aeration was given via pure air flow and by turning over the piles at an interval of 7 days. The piles have been protected with a layer of sawdust and straw on the floor to keep away from odors and affect from wind.
Composting
The composting course of lasted for a interval of 14 weeks, together with 4 levels such as the preliminary part, the thermophilic part, finish of thermophilic part and the mesophilic part. The sludge – conditioner combination was positioned on a mattress of wire mesh, at an altitude of 30 cm. The materials was unfold on a layer of wooden shavings, which was coated with a layer of sawdust and straw. The moisture content material was initially adjusted to 55% and later there was no addition of water. Once the pile was arrange, the decomposition of the natural matter by thermophillic microorganisms began, which elevated the temperature to 58° C, inflicting the destruction of the pathogens.
The cardio situations have been assured by aeration via turning. Thermophillic part remained for a interval of 50 days within the pile. Within a interval of 14 weeks, full stability of the compost and the removing of odors have been assured. The mixtures have been then saved for an additional 6 weeks for maturation. All the parameters have been assessed for this matured compost. Sifting was executed to matured compost to separate the conditioning materials and to acquire a homogenous product. Samples from composting mixtures have been analyzed as soon as each 7 days. A consultant pattern was taken by selecting up materials from completely different factors of the 2 piles.
Analytical Methods
All the parameters such as moisture content material, electrical conductivity, pH, natural matter, and nitrate nitrogen have been estimated utilizing customary APHA strategies [15]. Total Kjeldahl nitrogen and ammonical nitrogen have been analysed utilizing Kjeldahl meeting (Kjel Plus DISTILL M KPS 020, India), the oxidizable carbon (Co) was decided by oxidimetric methodology the ash content material by gravimetric methodology after burning off the dry mass at 550° C [16]. In the water extracts (compost/water ratio of 1:10) the water soluble varieties of carbon (Cw) and nitrogen (Nw) have been decided. Total phosphorous (ascorbic acid methodology) and cation trade capability (CEC) was decided in keeping with the tactic described by Gupta [17].
Humic Substances
Humic acids, Fulvic acids and non humic fraction have been estimated by the tactic as described by Hsu and Lo [18]. Humification index (HI), i.e., the ratio between Humic acids and fulvic acids is deduced from the equation:HI=HA/FAHumification Ratio=Extractable Carbon/TotalOrganic Carbon×100
Water-Soluble Carbon (Cw)
20 gms of compost was weighed and extracted with 200ml of deionized water by shaking for 24 hrs. The extracts have been centrifuged at 10,000 RPM for 25 minutes and filtered via 0.45-μm filter membranes (mdi, India). Water extracts are instantly analysed for natural carbon [18].
Enzyme Assay and Measurement
Assays of hydrolases (β-Glucosidase, BAA-Hydrolyzing Protease, Urease and Phosphatase) and dehydrogenase actions have been carried out as described by Garcia et al., [19, 20]. Dehydrogenase assay was based mostly on the mixture of two strategies [21,22]. To decide β-Glucosidase exercise 0.05 M 4-nitrophenyl-β-D- gluconopyranoside (PNG) was used as substrate [23] whereas,0.115 M p-nitrophenyl-phosphate (PNPP) was used as substrate to measure the phosphatase exercise. The para-nitrophenol (PNP) produced by each hydrolases was extracted and decided spectrophotometrically at 398 nm. [24]. To decide the BAA-hydrolysing Protease and Urease actions, 0.03 M N-α-Benzoyl-L-Argininamide (BAA) and 6.4% urea, respectively have been used as substrates. The ammonium launched by the 2 hydrolytic reactions was measured by an ammonium selective electrode (ORION, Model.95–12). To decide dehydrogenase exercise, 0.4% 2-p-iodophenyl-3-p-nitrophenyl-5-tetrazolium chloride (INT) was used as substrate. Iodonitrotetrazolium formazan (INTF) produced within the discount of INT was measured spectrophotometrically at 490 nm.
Germination Index
The absence of phyto-inhibitory substances that mirror maturity of compost was examined by seed germination. Germination checks have been carried out with backyard cress (Lepidium sativum L.) Seeds have been soaked in compost extracts in water (1: 10 w/v) for 48 h. Lepidium sativum seeds have been used as a result of of their speedy germination and sensitivity to phytotoxic compounds [25]. The germination index, inversely associated to the presence of phytotoxic substances in compost, was calculated as the proportion of seeds germinated on filter paper in Petri dishes with 10 ml of compost extract multiplied by the common size of roots in mm expressed as share of a management with distilled water [26]. The percentages of relative seed germination, relative root elongation and germination index (GI) are calculated by the next method:No of seeds germinated in extractRelative seed germination (%)=—————X 100No of seeds germinated in controlMean root size in extractRelative Root Growth (%)=———————X 100Imply root size in management(%Seed Germination)×(%RootGrowth)Germination Index=——————————-100
Results and Discussion
The physico chemical evaluation of the manure and noticed mud and sediments from two completely different strata used within the current research are offered in Table 2 and Table 3 respectively. A consultant pattern was taken by selecting up materials from completely different factors of the 2 piles.
Temperature, Moisture Content, Ph & Electrical Conductivity
The temperature variation throughout composting adopted a sample much like many different composting techniques [27, 28]. In Pile 1 the temperature rised solely upto 46° as a result of of the presence of extremely poisonous compounds and thus low microbial exercise whereas in pile 2 there was a steep improve in temperature as much as 58° as a result of availability of comparatively extra degradable natural matter and therefore intense microbial exercise. The thermophillic part lasted for almost 7 weeks. After this era of elevation the temperature regularly decreased to ambient ranges and this marked the top of the thermophilic part of composting. At this stage the decomposition charge stabilized with a consequent lower in temperature and microbial actions.
During composting the moisture content material of the piles decreased which is as a result of evaporation of water as a consequence of turning the piles and microbial warmth era. The steady lower in moisture content material throughout composting is a sign of natural matter decomposition [29]. The moisture content material in Pile 1 decreased as much as 42% whereas that in Pile 2 decreased to 30%. The intense microbial exercise and natural matter degradation through the first weeks of thermophilic part led to the formation of ammonia as a consequence of ammonification of natural nitrogen. The solubilzation of ammonia led to the formation of ammonium and a rise within the pH values within the composting mixtures from an preliminary of 6.Eight to 7.6 in pile 1 and from 6.7 to eight.2 in pile 2. Electrical conductivity elevated as a result of focus of the salts as a result of of degradation of natural matter [51]. Production of Nitrate-N additionally explains the rise in conductivity of the composting mixtures. This is necessary from an agricultural level of view since a rise in electrical conductivity is a direct consequence of the elevated focus of vitamins, such as nitrate.
Changes within the Carbon/Nitrogen Ratio & Compost Mineralization Index
The modifications within the C/N ratio mirror natural matter decomposition and stabilization throughout composting and are represented in Figure 2. In the preliminary stage of composting intense mineralization processes takes place which is manifested by a substantial lower in carbon and improve in ash content material in each the piles, the C/N ratio decreased as a result of mineralization of the natural matter [30]. The complete nitrogen content material elevated throughout composting from an preliminary of 1.6% to 1.75% in pile 1 and from 1.65% to 1.76% in Pile 2. These nitrogen will increase are in all probability because of a focus impact brought on by the lower of the substrate carbon ensuing from CO2 misplaced [31] as a consequence of the degradation of non-nitrogenous natural matter (Carbohydrates and many others.).
The natural carbon focus in Pile 2 degraded way more intensely through the thermophillic part of composting because of higher exercise of the micro organisms and the presence of simply degradable substances. After 14 weeks of composting the natural matter in Piles 1 and 2 decreased from 48.9% to 34% and from 48% to 21% respectively. The C/N ratio decreased as a result of mineralization of the natural matter. In pile 1 the Carbon/Nitrogen decreased from an preliminary worth of 30.5 to 19.Four on the finish of the method whereas for a similar interval of time in pile 2 the preliminary carbon/nitrogen ratio decreased from 29.5 to 11.9. According to [32] a Carbon/Nitrogen within the vary of 10–15 of the compost signifies a great diploma of maturity.
The compost mineralization index is expressed as Ash content material/Oxidizable Carbon. The modifications in Compost Mineralization Index are represented in Figure 5. In the preliminary stage of composting (about 7 weeks) the extraordinary mineralization course of takes place, which is manifested by a substantial lower in carbon and improve in ash content material. In Pile 1 the ash content material elevated from 45.1% to 52.8% and the oxidizable carbon decreased from 19.5% to 16.2% the compost mineralization index elevated from 1.85 to three.01. The ash content material in Pile 2 elevated from 49.4% to 61.9% and the oxidizable carbon lower from 20.4% to 14.1% and the compost mineralization index elevated from 2.5 to 4.65.
Nitrification Index
The nitrification course of has been used as maturity index of composting [33]. The modifications in Nitrification Index expressed as NO3− -N/NH4+ -N through the composting course of is offered in Figure 2. The NH4+ – N content material in pile 2 elevated from 658 mg/kg to 725 mg/kg through the thermophilic part. This improve might be because of conversion of natural N to NH4+ -N through the ammonification course of and then the NH4+ – N content material decreased to 144 mg/kg in direction of the top of maturation part. The same pattern was noticed by [34, 35]. This lowering pattern assured that ammonification was ending and can be utilized as a criterion of compost maturity [36]. The ammonia produced through the thermophilic part is oxidized to NO3− -N and thus the focus of ammonia decreases with the rise in NO3− -N. In Pile 1 the rise in ammonical nitrogen was not very vital and so was the lower. The NO2 focus was negligible in each the piles, indicating that cardio situations prevailed through the composting course of.
Appreciable quantities of NO3− – N might be noticed in Pile 2 the values elevated from 0.01% to 4.5%, which have been reached after maturation. A NH4+/NO3− ratio in favour of the oxidized kind is taken into account fascinating for mature compost. In Pile 1 the NH4+/NO3− ratio was 0.28 whereas in Pile 2 the ratio was 0.03 in direction of the top of composting. At the top of the method the focus of nitrates must be larger than that of ammonium indicating that the method has been ready underneath satisfactory situations of aeration [29]. Due to the presence of extremely poisonous organics in Pile 1 there was low mineralization of natural nitrogen which in flip resulted in low ammonia evolution whereas in Pile 2 low focus of organics resulted I larger nitrogen mineralization and therefore larger ammonia evolution A excessive focus of NH4- N in compost signifies instability and in keeping with Zucconi & Bertoldi [12] it shouldn’t exceed 0.04% in mature compost [33] established a restrict a 0.16 as a ratio between ammonium nitrogen and nitric nitrogen as an index of maturity in composts.
Water Soluble Carbon (Cw)
The water-soluble carbon variation with composting time is offered in Figure 3. Water–soluble natural carbon is probably the most readily biologically lively compound in composts utilized to soils. Water-soluble natural carbon degree in Pile 1 regularly elevated from 1.35% to 1.44% within the 7th week and then regularly decreased to 1.29% in direction of the top. While in Pile 2 the water-soluble natural carbon degree regularly elevated from 2.02% to 2.41% within the 7th week and then regularly decreased to 1.32% in direction of the maturation part.
As carbon element which might be simply out there to microbes natural and amino acids, proteins have been degraded through the thermophillic stage of the decomposition, breakdown merchandise have been constantly launched leading to a rise in water-soluble carbon [18]. A decline in water-soluble carbon is commonly used as an indicator of compost maturity [37]. In matured compost most of the soluble natural carbon is current as humic substances, that are immune to additional decomposition, thus explaining its elevated stability noticed with time throughout composting. A restrict of Cw < 1.7% can be utilized to mirror a great maturation diploma. [33].
CNw (Water soluble)
The water-soluble carbon and nitrogen index is offered in Figure 3. Water-soluble natural carbon degree in Pile 1 regularly decreased by about 4.4% whereas in Pile 2 the lower was 34.6%. The simply biodegradable carbon elements which might be extremely out there to microbes have been degraded through the thermophillic stage of the decomposition, and the breakdown merchandise have been constantly launched leading to a rise in water-soluble carbon [18]. During composting the whole nitrogen content material will increase with simultaneous lower of its solubility in water (Nw) and in direction of the maturation part the quantity of mineral water soluble varieties of nitrogen elevated. [16]. In Pile 1 the Nw lower kind 13.5% to 7.2% and in Pile 2 the lower was kind 13.5% to five.0%. The CNw elevated from 0.99 to 1,7 in Pile 1 whereas in Pile 2 the CNw elevated from 1.Four to 2.6 on the finish of composting interval.
Humic Substance Content
Humic substances comprise an important fraction of natural matter as a result of of their distinctive properties, such as the capability to work together with steel ions, the power to buffer pH, and the power to behave as a possible supply of vitamins for crops [18]. The relative contents of humic substances and non-humic substances throughout composting are offered in Figure 4. The portions of Humic acids, Fulvic acids and non-humic fraction in composting combination at varied levels of the composting course of characterize the humification course of.
In Pile 1 complete humic substances elevated from 15% of natural matter to 25% of natural matter after 7 weeks, stabilizing at this worth until the top of the method. The fulvic acid degree regularly decreased from 6.1% of natural matter to five.4% in mature compost. The humic acid degree elevated from 3.2% to 10.8% within the mature compost.
In Pile 2 Total humic substances elevated from 31% of natural matter to 52% of natural matter after 7 weeks, stabilizing at this worth until the top of the method. The fulvic acid regularly decreased from 8.2% of natural matter to five.4% in mature compost. The humic acids elevated from 5.2 to 21.9% within the mature compost.
The rising degree of humic acids throughout composting course of represents the humification and maturity of compost. In basic, contemporary composts comprise low ranges of humic acids and larger ranges of fulvic acids [10]. During composting humic acids elevated, the place as fulvic acids barely decreased. The non humic fraction in Pile 1 elevated quickly from 14% to 17% however then didn’t lower additional because of low natural matter degradation. in Pile 2 non humic fraction elevated quickly from 18% to 30% of natural matter for the primary 7 weeks of composting, and then decreased to 12% within the mature compost could also be because of decomposition and humification of the break down merchandise and presence of simply biodegradable natural matter through the maturation stage.
The Humification index and Humification ratio of the 2 piles are offered in Figure 8. Humification index in Pile 1 remained regular at 0.6–0.7 for the primary Four weeks and elevated sharply to 1.Three within the seventh week and slowly elevated to a remaining worth of 1.Eight in direction of maturity of compost. Humification index in Pile 2 remained regular at 0.6–0.Eight for the primary Four weeks and elevated sharply to 1.Eight within the seventh week and slowly elevated to a remaining worth of 4.Zero in direction of maturity of compost. The modifications in humification index reveal that Fulvic fraction and non humic fraction extracted from sediment comprise comparatively excessive ranges of biodegradable natural matter that was largely decomposed throughout first 7 weeks of composting. The humification ratio in Pile 1 elevated from 0.29 to 0.94 whereas in Pile 2 it elevated from 0.Four to 1.04.
Cation Exchange Capacity & Sorption Capacity Index
One of the variables which might be often decided to estimate the diploma of transformation reached by compost through the course of of composting is cation trade capability (CEC). The modifications in cation trade capability are offered in Figure 9. Its dedication in an natural modification is of nice worth as a result of it permits us to know the soundness diploma of the modification. Several research achieved with completely different varieties of compost have demonstrated that CEC will increase with the soundness diploma of the compost. On the opposite hand, this parameter provides a sign of the modification’s capability for catching vitamins and immobilizing phytotoxic substances as nicely as for buffering unexpected pH modifications.
The obtained outcomes confirmed that the CEC elevated from an preliminary worth of 31cmol/kg−1 to remaining values of 38.9cmol kg−1 in Pile 1 whereas in Pile 2 the worth elevated from an preliminary worth of 55.Three to 68.6 cmol kg−1. The worth within the Pile 2 was larger than the minimal really useful for mature compost (67 cmol kg−1) thus indicating that the compost is mature [11, 52].
The Cation Exchange Capacity/Corganic ratio displays the diploma of maturity of particular humic compounds and in keeping with Inbar et al., [38] it may be linked with the rise of the practical teams throughout humification course of. The cation trade capability will increase and natural carbon decreases with composting. The modifications in Sorption Capacity Index are represented in Figure 5. At the top of the lively part Pile 1 had a sorption capability index of 1.1 whereas Pile 2 had a worth of 3.2 which was higher than 1.7 the bottom restrict for describing nicely humified manures [11].
Germination Index (GI)
The GI values elevated through the composting course of because of decomposition of the phytotoxic natural compounds. The change in germination index is offered in Figure 9. These phytotoxic compounds, which have been current in uncooked waste or produced through the first days of composting as intermediate merchandise of microbial metabolism, have been degraded through the course of, giving mature composts, which might safely be used with crops. The pattern taken from the Piles 1 had GI a of 49 whereas Pile 2 had a GI of 95 which is larger than 80 and in keeping with Zucconi et al., [25] & Tiquia et al., [39] signifies a phytotoxic-free compost.
Profiles of Enzymatic Activities
The degradation of the labile substrates contained in natural matter may be adopted by finding out particular hydrolases, that are comparatively simple to find out, and particular to the substrate. The hydrolases monitored within the current work (BAA-Hydrolysing Protease, Urease, β-glucosidase, Dehydrogenase and Phosphatase might characterize a great index of qualitative fluctuations of substrate throughout composting since they’re substrate-inducible enzymes. The modifications in enzymatic actions in Pile 1 and 2 are proven in Fig. 6. The excessive preliminary exercise of these enzymes mirrored the excessive microbial exercise. The presence of a excessive content material of degradable compounds within the pile 2 might need stimulated enzyme synthesis. As substrate decreased, the enzyme exercise decreased as nicely [40].
The β-glucosidase exercise decreased all through the composting course of, in Pile 2 as could also be anticipated, since carbonated constructions are degraded as composting proceeded and solely probably the most resistant and these with the smallest quantity of facet chains stay on the finish of the method. β-Glucosidase and BAA-hydrolyzing protease that are enzymes concerned in C and N cycles, respectively confirmed a pointy lower through the first 7 weeks, and then stabilized as a consequence of lower in out there natural substrates [41].
Urease exercise is intently associated with the nitrogen cycle and it’s concerned within the hydrolysis of proteins to ammonium hydrolyzing urea-type substrates. It is believed that denaturalization of the enzyme throughout composting because of excessive temperature doesn’t happen since urease is secure as much as 80° C [42]. There is a pronounced distinction between the values of the preliminary and composted samples.
This is maybe as a result of the enzyme is determined by microbial biomass, which means that when the biomass is degraded (because of composting) enzymatic exercise decreases. The exercise of urease which catalyses the hydrolysis of urea to CO2 and NH4+, elevated through the first Four weeks of experiment in all probability as a consequence of diminution of excessive preliminary focus of NH4+ within the substrate which can be accountable for the inhibition of this exercise [43]. Subsequently urease exercise decreased till week 7 and then remained roughly secure until the terminal part of the composting course of.
Phosphatase is a key enzyme within the phosphorus cycle, which is induced by the substrate. Its exercise is essentially depending on microbial biomass [40]. Phosphatase exercise confirmed a pointy improve through the thermophilic part adopted by a gradual lower. The improve noticed through the thermophillic part may be related to excessive microbial exercise, which happens throughout this stage. The phosphatase hydrolyses compounds of natural phosphorous and transforms them into completely different varieties of inorganic phosphorous [44]. Thus, the lower in exercise noticed may be because of enzyme inhibition by inorganic phosphorous quickly launched from the mineralization of the natural phosphorous [45]. Phosphatases are enzymes with comparatively broad specificity succesful of hydrolyzing varied natural phosphate esters [46]. The excessive preliminary exercise might be associated to the presence of natural phosphate compounds which can act as inducers of enzyme synthesis after a slight lower through the first week phosphate exercise stabilized at about 200 μmol PNP g−1 h−1 in Pile 2 and at 260 μmol PNP g−1 h−1 in Pile 1 [19].
Dehydrogenase exercise in soils and different organic techniques has been used as a measure of the general microbial exercise [47] since it’s an intracellular enzyme associated to the oxidative phosphorylation course of [48]. The preliminary excessive dehydrogenase exercise recorded might need been the end result of excessive microbial exercise as a result of excessive water soluble carbon focus after two weeks dehydrogenase exercise decreased till the top of composting. The dehydrogenase exercise is represented in Figure 7.
Characterization of Final Compost
A quantity of bodily, chemical and organic indices have been linked to the maturity of composts [49]. The compost in Pile 2 was alkaline, pleasantly earthy in scent and darkish down. Compost traits are offered in Table 2. From the outcomes obtained, compost in Pile 2 confirmed a C/N ratio of 11.9, which is in accordance with the really useful worth between 10 and 15 [32]. This signifies that there’s a appreciable lower in natural matter, water-soluble carbon and nitrogen. A complete N content material in composts is larger than the minimal degree really useful (0.6% complete N) by Zucconi and De Bertoldi [12]. Enzymatic actions noticed within the current research are intracellular actions of proliferating microorganisms and not as a result of actions of further mobile enzymes. Hence hydrolytic and dehydrogenase actions are delicate indicators of the state and evolution of the natural matter and the general high quality of the compost. The macronutrient contents have been above the minimal really useful (0.5% P2O5; 0.3% Ok2O; 0.3% Ok2O; 0.3% MgO; 2.0% CaO) by Zucconi and De Bertoldi [at high pH conditions [50]. Heavy metals current, in 12]. Metal mobility and availability was decreased by elevated pH values since cationic ions are much less out there all of the composts, have been under the utmost values permitted for every factor. Further research on the regulatory requirements of the composted product can validate the applicability of these stabilized sediments for profitable software as biosolids.
Cost of Treatment
The tentative price of the remedy is calculated for your entire lake space of 0.5 Km2 from the research carried out in lab scale. The lakebed is extra polluted at sure quartets and in direction of the inlet and outlet culverts. From our research solely 50% of the lake space wants dredging to a depth of 0.25m and the amount of the whole sediment to be dredged shall be 31,250 m3. The estimate price for dredging and transportation of the polluted sediment to TSDF is Rs7, 00,00,000/-(US$16,00,000). The price for ploughing your entire lake space to a depth of 0.6m is Rs 2,00,00,000/- (US$4,50,000). The complete price of rejuvenation of the lake by liming, composting and additional organic exercise is calculated to be Rs 1,00,00,000/- (US$2,30,000). Therefore the approximate price calculated from our research Rs 10,00,00,000/-(US$ 22,80,000). The price of the remedy calculated is an extrapolation from our research carried out underneath lab situation and is subjected to range with the character of the pollution.
Conclusions
Remediation of contaminated lake sediments utilizing bioremediation generally is a price efficient resolution. The current research envisaged on the applicability of this expertise for your entire lake insitu by finishing up lab scale research of completely different stratum. The research revealed that the after the elimination of the highest layer for physicochemical remedy the decrease layers confirmed lowering ranges of focus with depth indicating the gradual transport charge of the pollutant.
Aerobic composting, a bioremediation expertise adopted within the current research was discovered to be very efficient for the underside layers and was vital for the highest layers. Hence from our research it’s concluded that my mixing your entire lakebed with a standard farming method referred to as as “Ploughing”, and pretreatment with lime can render the stabilization of steel pollution. However, liming could not utterly stabilize metals within the case of lake beds contaminated with larger steel concentrations. Thus the stabilization of these lakes needs to be addressed on pollutant particular situations with integration of physico-chemical and organic stabilization methodologies. The success of the composting of lake sediments was achieved by optimizing the C/N ratio of the piles to 30:1, moisture content material of 55%. Further addition of bulking brokers and natural amendments within the ratio of 2:1:1 (Sediment: sawdust: manure).
The success of the composting maturity was assessed by evaluating indices C/N, Cw (water soluble carbon), CNw (Cw/Nw), nitrification index (NH4/NO−3), Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC), germination index, humification ratio, compost mineralization index (ash content material/oxidizable carbon), sorption capability index (CEC/oxidizable carbon). Enzyme actions of agricultural curiosity like urease, phosphatase, β-glucosidase, dehydrogenase and BAA-hydrolyzing protease, that are concerned within the nitrogen, phosphorus and carbon cycles, have been additionally assessed. Total content material of macro and micronutrients within the remaining compost was additionally decided to evaluate the fertilizer worth.
The indices are in contrast with the literature values and may be concluded that the maturity indices are helpful indicators for the success of the composting expertise. The deal with potential of the contaminated sediment may be evaluated utilizing these indices and on standardizing these indicators may be efficiently relevant for prototype software. The research additionally made an try to work out the fee of this remedy possibility. Thus it may be concluded that remedy of contaminated lake sediments must be addressed as case-by-case situation. Bioremediation coupled with different physico-chemical and rising applied sciences may be an efficient insitu resolution in dealing with the remediation of the pure water our bodies and carry them again to life to assist different dependent techniques.