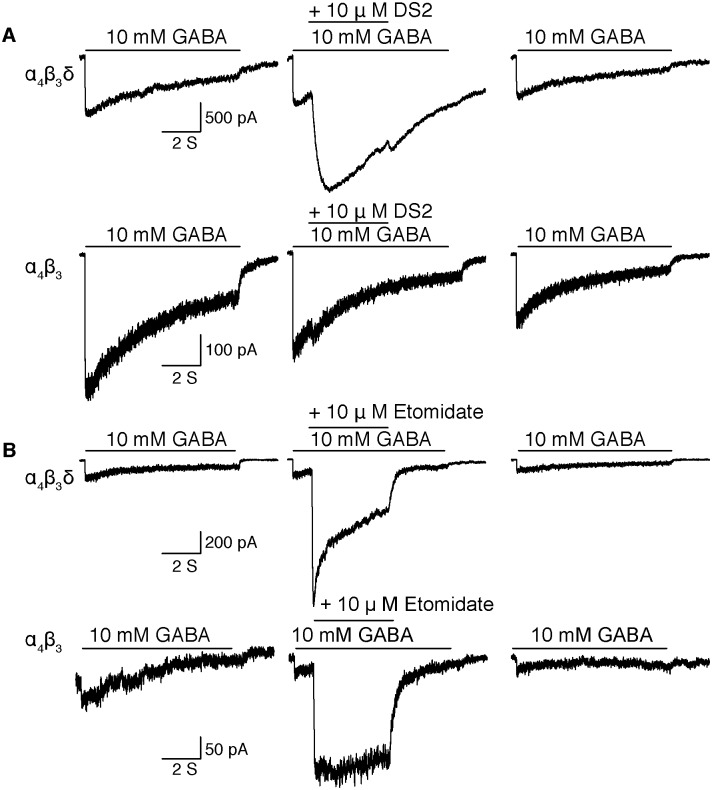
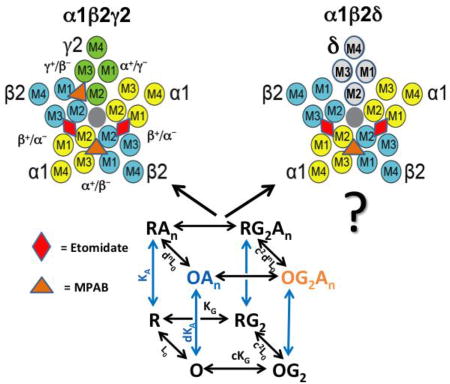
High-level production and purification in a functional state of an extrasynaptic gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor containing α4β3δ subunits.
The inhibitory γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors are implicated in numerous physiological processes, including cognition and inhibition of neurotransmission, rendering them important molecular targets for many classes of drugs. Functionally, the entire GABAAR family of receptors can be subdivided into phasic, fast acting synaptic receptors, composed of α-, β- and γ-subunits, and tonic extrasynaptic receptors, many […]